Does Multiple Sclerosis Cause Weight Gain?
🚨 Attention, MS Warriors and Health Enthusiasts! 🚨
Are you battling Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and noticing unexpected changes on the scale? You’re not alone. The hidden link between MS and weight gain is a topic that’s been lurking in the shadows, leaving many patients puzzled and frustrated. But what if we told you that there’s more to this connection than meets the eye?
Prepare to have your mind blown as we uncover 5 shocking truths about MS and weight gain. From medication side effects to hormonal imbalances, we’re diving deep into the complex web of factors that could be impacting your weight. Whether you’re living with MS or simply curious about this intriguing health connection, this blog post will shed light on a topic that’s been shrouded in mystery for far too long. Get ready to embark on a journey of discovery as we explore the intricate relationship between Multiple Sclerosis and those stubborn extra pounds.

Understanding the MS-Weight Connection
A. Defining Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, primarily the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. In MS, the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body.
B. The prevalence of weight gain in MS
Weight gain is a common concern among individuals with MS. Studies have shown that:
- Approximately 50% of MS patients are overweight or obese
- Weight gain tends to increase as the disease progresses
- BMI in MS patients is often higher than in the general population
| MS Stage | % of Patients Experiencing Weight Gain |
|---|---|
| Early | 25-30% |
| Advanced | 40-50% |
C. Common weight-related concerns in MS patients
MS patients often face several weight-related challenges:
- Reduced mobility leading to decreased physical activity
- Fatigue limiting exercise and daily activities
- Medication side effects contributing to weight gain
- Hormonal imbalances affecting metabolism
- Emotional and psychological factors influencing eating habits
These factors can create a complex interplay, making weight management particularly challenging for individuals with MS. Understanding these connections is crucial for developing effective strategies to maintain a healthy weight while managing the symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
Uncovering the First Shocking Truth: Medication Side Effects
As we delve deeper into the relationship between multiple sclerosis (MS) and weight gain, we encounter a startling revelation: many medications used to treat MS can contribute to weight fluctuations. This hidden link often catches patients off guard, making it crucial to understand the potential side effects of common MS treatments.
Antidepressants and weight fluctuations
Antidepressants, frequently prescribed to MS patients to manage depression and mood disorders, can significantly impact weight. Here’s a breakdown of common antidepressants and their effects on weight:
| Antidepressant Type | Weight Effect | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| SSRIs | Modest weight gain | Fluoxetine, Sertraline |
| SNRIs | Minimal weight change | Venlafaxine, Duloxetine |
| TCAs | Significant weight gain | Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline |
It’s important to note that individual responses may vary, and not all patients will experience weight changes.
Disease-modifying therapies and their impact
Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are crucial in managing MS progression. However, some DMTs can affect weight:
- Interferon beta medications: May cause initial weight loss followed by gradual weight gain
- Glatiramer acetate: Generally weight-neutral
- Dimethyl fumarate: Can lead to weight loss in some patients
- Teriflunomide: May cause weight loss in the first three months of treatment
Corticosteroids and weight gain
Corticosteroids, often used to manage MS relapses, are notorious for their weight-related side effects:
- Increased appetite
- Fluid retention
- Altered fat distribution (especially around the face and abdomen)
- Potential long-term metabolic changes
These effects can be particularly pronounced with high-dose, long-term corticosteroid use. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to minimize these side effects while maximizing treatment benefits.
Understanding these medication-related weight changes is crucial for MS patients. With this knowledge, we can now explore how mobility limitations further compound the weight management challenges faced by those with MS.
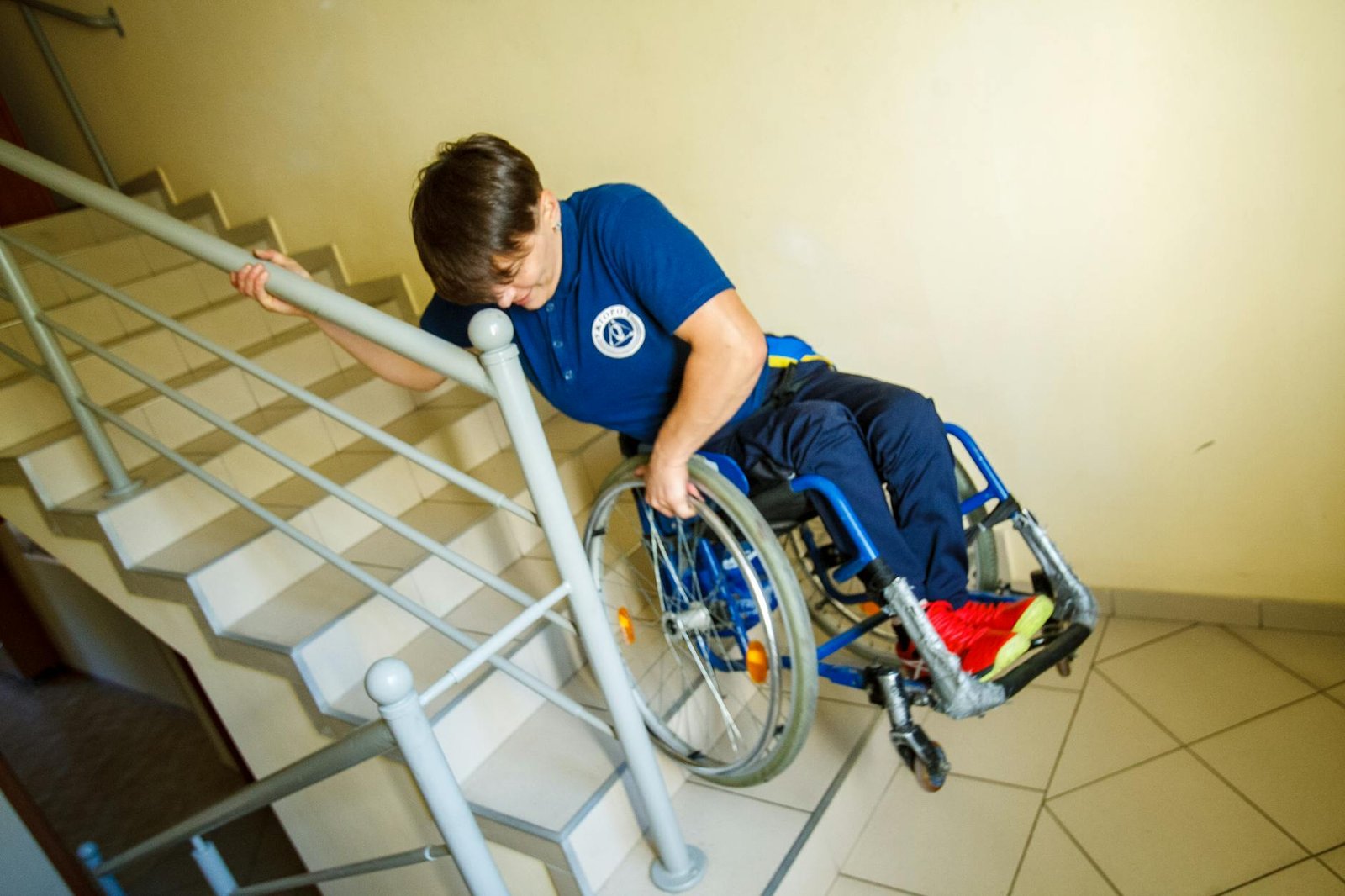

Revealing the Second Shocking Truth: Mobility Limitations
As we delve deeper into the relationship between multiple sclerosis (MS) and weight gain, we encounter a crucial factor: mobility limitations. This shocking truth reveals how reduced physical activity can significantly impact weight management for MS patients.
How MS affects physical activity
Multiple sclerosis can severely restrict a person’s ability to move freely and engage in regular physical activities. This limitation stems from various MS symptoms, including:
- Muscle weakness
- Spasticity
- Balance issues
- Coordination problems
- Fatigue
These symptoms can make it challenging for individuals with MS to maintain an active lifestyle, leading to a more sedentary routine and potential weight gain.
The impact of reduced mobility on metabolism
Reduced physical activity due to MS-related mobility limitations can have a significant effect on metabolism:
| Metabolic Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Decreased muscle mass | Less physical activity leads to muscle atrophy, reducing overall metabolic rate |
| Lower energy expenditure | Fewer calories burned throughout the day due to reduced movement |
| Altered hormone balance | Changes in hormones that regulate metabolism and appetite |
These metabolic changes can create a perfect storm for weight gain in MS patients, making it crucial to address mobility issues proactively.
Strategies to stay active with MS
Despite the challenges, there are several ways for individuals with MS to maintain an active lifestyle:
- Adaptive exercises: Tailored workouts that accommodate mobility limitations
- Aquatic therapy: Water-based exercises that reduce stress on joints and muscles
- Seated exercises: Chair-based workouts for those with limited standing ability
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance
- Assistive devices: Using mobility aids to increase independence and activity levels
By implementing these strategies, MS patients can work towards maintaining a healthy weight despite mobility limitations. Remember, even small amounts of regular physical activity can make a significant difference in managing weight and overall health.
Now that we’ve uncovered the impact of mobility limitations on weight gain in MS, let’s explore another crucial factor: the role of fatigue in this complex equation.

Exposing the Third Shocking Truth: Fatigue and Its Role
Fatigue is a common and often debilitating symptom of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) that can significantly impact a person’s daily life and, surprisingly, their weight. Let’s delve into how fatigue contributes to weight gain in MS patients and explore strategies to manage this challenging symptom.
Understanding MS-related fatigue
MS-related fatigue is not your typical tiredness. It’s an overwhelming sense of exhaustion that can occur suddenly and without warning. This fatigue can be:
- Physical: Affecting muscle strength and endurance
- Cognitive: Impairing concentration and mental clarity
- Persistent: Lasting for extended periods and not relieved by rest
How fatigue contributes to weight gain
Fatigue can lead to weight gain in MS patients through various mechanisms:
- Reduced physical activity
- Increased reliance on convenience foods
- Disrupted sleep patterns
- Altered metabolism
| Fatigue-related factor | Impact on weight |
|---|---|
| Reduced activity | Decreased calorie burn |
| Convenience foods | Higher calorie intake |
| Sleep disruption | Hormonal imbalances |
| Altered metabolism | Slower calorie burning |
Managing fatigue to control weight
To effectively manage weight while dealing with MS-related fatigue, consider these strategies:
- Plan energy-efficient meals
- Incorporate gentle exercises like yoga or swimming
- Practice good sleep hygiene
- Use assistive devices to conserve energy
- Work with a nutritionist to develop a balanced, easy-to-prepare meal plan
By understanding the role of fatigue in weight gain and implementing these management strategies, MS patients can better control their weight while coping with this challenging symptom. Now that we’ve uncovered the impact of fatigue, let’s explore another surprising factor in MS-related weight gain: hormonal imbalances.
Discovering the Fourth Shocking Truth: Hormonal Imbalances
As we delve deeper into the complex relationship between Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and weight gain, we uncover a lesser-known factor: hormonal imbalances. This surprising connection plays a significant role in the weight management challenges faced by MS patients.
Addressing hormonal issues in MS patients
MS can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body, leading to unexpected weight fluctuations. Here’s a breakdown of the most common hormonal imbalances in MS patients:
| Hormone | Effect on Weight | Prevalence in MS |
|---|---|---|
| Cortisol | Increased fat storage | High |
| Thyroid hormones | Slowed metabolism | Moderate |
| Leptin | Impaired appetite regulation | Variable |
Cortisol levels and their effect on weight
Cortisol, often called the “stress hormone,” plays a crucial role in weight gain for MS patients:
- Elevated cortisol levels are common in MS due to chronic inflammation and stress
- High cortisol promotes fat storage, especially around the abdomen
- It can increase appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods
To manage cortisol-related weight gain, MS patients can:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Incorporate regular, moderate exercise into their routine
MS and thyroid function
Thyroid dysfunction is another hormonal factor that can contribute to weight gain in MS patients:
- MS can increase the risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disorders
- Hypothyroidism, a common thyroid issue, can slow metabolism and lead to weight gain
- Regular thyroid function tests are crucial for MS patients to detect and address any imbalances
Understanding these hormonal factors is essential for developing effective weight management strategies for MS patients. By addressing these imbalances, individuals can take a more targeted approach to maintaining a healthy weight while managing their MS symptoms.

Unveiling the Fifth Shocking Truth: Emotional and Psychological Factors
The emotional and psychological impact of living with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) can significantly influence weight gain. This often-overlooked aspect of MS management plays a crucial role in understanding the complex relationship between the disease and body weight.
A. Developing healthy coping mechanisms
Developing healthy coping mechanisms is essential for MS patients to manage their emotional well-being and maintain a healthy weight. Here are some effective strategies:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Regular exercise (adapted to individual abilities)
- Joining support groups
- Engaging in creative activities
- Practicing stress-reduction techniques
B. Stress-eating and its consequences
Stress-eating is a common challenge for many MS patients, leading to unintended weight gain. The consequences of this behavior can be significant:
| Consequence | Impact on MS Patients |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Increased fatigue and mobility issues |
| Nutritional imbalances | Exacerbation of MS symptoms |
| Emotional distress | Heightened anxiety and depression |
| Reduced medication efficacy | Potential worsening of MS progression |
C. Depression and anxiety in MS
Depression and anxiety are prevalent among MS patients and can contribute to weight gain in several ways:
- Reduced motivation for physical activity
- Increased appetite due to certain antidepressants
- Emotional eating as a coping mechanism
- Disrupted sleep patterns affecting metabolism
Recognizing and addressing these emotional and psychological factors is crucial for effective weight management in MS patients. By developing healthy coping strategies, managing stress-eating, and addressing depression and anxiety, individuals with MS can better control their weight and improve their overall quality of life.

Effective Weight Management Strategies for MS Patients
Now that we’ve explored the shocking truths behind weight gain in multiple sclerosis, let’s focus on practical strategies to manage weight effectively for MS patients.
A. Mindfulness and stress reduction techniques
Incorporating mindfulness practices into daily routines can significantly impact weight management for MS patients. These techniques not only help reduce stress but also promote better eating habits and overall well-being.
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Yoga (modified for MS patients)
B. Working with healthcare professionals
Collaborating with a multidisciplinary healthcare team is crucial for developing a personalized weight management plan. This team may include:
| Professional | Role in Weight Management |
|---|---|
| Neurologist | Monitors MS progression and adjusts medications |
| Dietitian | Creates tailored nutrition plans |
| Physical Therapist | Designs adaptive exercise programs |
| Psychologist | Addresses emotional and psychological factors |
C. Adaptive exercise programs
Regular physical activity is essential for weight management in MS patients. Adaptive exercise programs cater to varying levels of mobility and energy:
- Water aerobics
- Chair exercises
- Resistance band workouts
- Low-impact cardio (e.g., stationary biking)
D. Tailored nutrition plans
A balanced diet is crucial for managing weight and supporting overall health in MS patients. Key components of a tailored nutrition plan include:
- Emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods
- Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids
- Ensuring adequate vitamin D intake
- Balancing macronutrients for energy management
By implementing these strategies and working closely with healthcare professionals, MS patients can effectively manage their weight and improve their quality of life. Remember, consistency and patience are key in achieving long-term success in weight management with MS.

The relationship between Multiple Sclerosis and weight gain is complex and multifaceted. As we’ve explored, medication side effects, mobility limitations, fatigue, hormonal imbalances, and emotional factors all play significant roles in this intricate connection. Understanding these shocking truths empowers MS patients to take proactive steps in managing their weight and overall health.
While the challenges may seem daunting, there are effective strategies available for MS patients to maintain a healthy weight. By working closely with healthcare providers, adopting tailored exercise routines, managing medication side effects, and addressing emotional well-being, individuals with MS can overcome these obstacles. Remember, every small step towards a healthier lifestyle contributes to improved quality of life and better management of MS symptoms.
Read More about Multiple Sclerosis
Read about 5 Shocking Truths About Multiple Sclerosis Infusion Treatments Your Doctor Won’t Tell You