Ankylosing Spondylitis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
Are you experiencing persistent joint pain and stiffness? You’re not alone. Millions of people worldwide grapple with chronic joint conditions, but two stand out as particularly challenging: Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). 🦴💪
While both conditions can significantly impact your quality of life, they’re often mistaken for each other due to their similar symptoms. This confusion can lead to delayed diagnosis and improper treatment, potentially worsening your condition. But fear not! Understanding the key differences between AS and RA is crucial for getting the right care and managing your symptoms effectively. 🏥🔍
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the battle of the joints: AS vs RA. We’ll explore their basic characteristics, diagnostic challenges, impact on daily life, and tailored treatment approaches. By the end, you’ll be armed with practical tips for living with these conditions and the knowledge to advocate for your health. Let’s embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of AS and RA! 🚀💡

Understanding the Basics: AS vs RA
Key differences in joint involvement
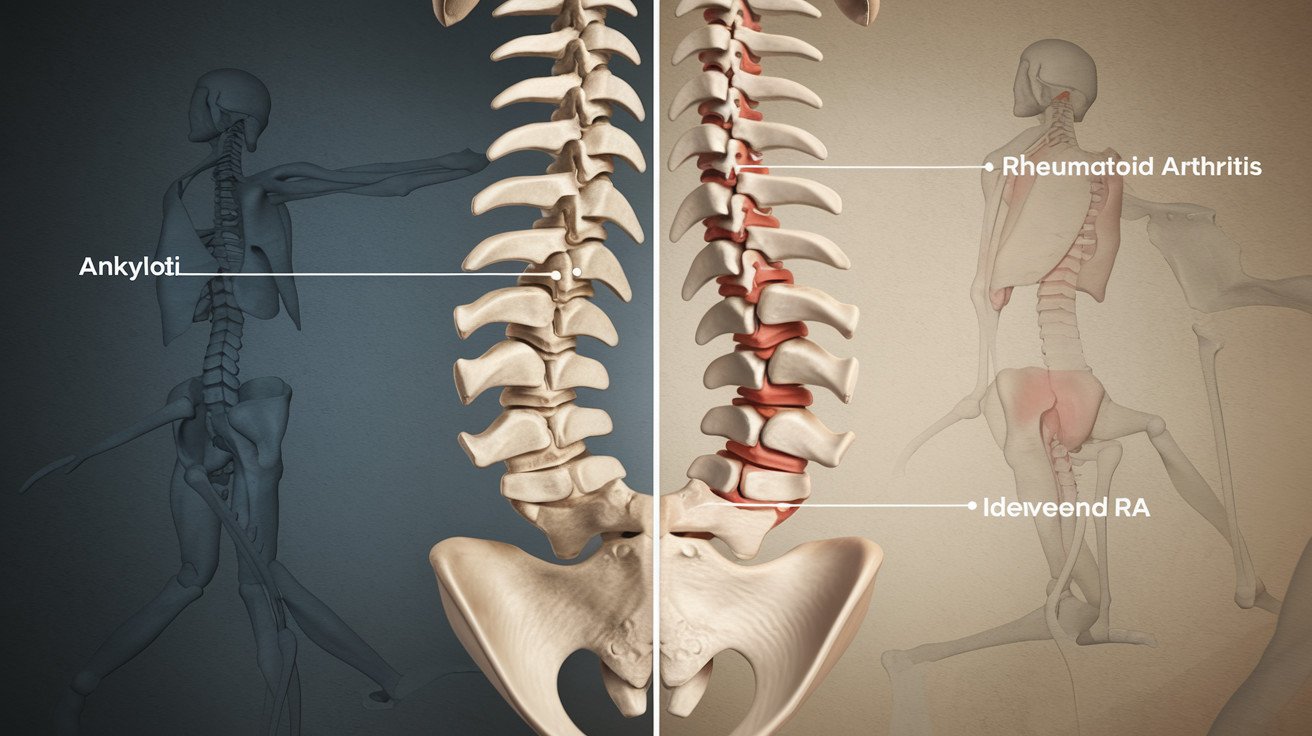
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) affect different parts of the body. AS primarily targets the spine and sacroiliac joints, while RA typically affects smaller joints in the hands and feet. This distinction is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
| Condition | Primary Joint Involvement |
|---|---|
| AS | Spine, sacroiliac joints |
| RA | Small joints of hands and feet |
Genetic factors and risk assessment
Both conditions have genetic components, but they differ in their specific genetic markers:
- AS is strongly associated with the HLA-B27 gene
- RA is linked to the HLA-DRB1 gene
Understanding these genetic factors can help in assessing an individual’s risk for developing either condition.
Age and gender prevalence
AS and RA exhibit different patterns in terms of age of onset and gender distribution:
- AS typically begins in late adolescence or early adulthood (15-45 years)
- RA can occur at any age but often starts between 30-60 years
Gender prevalence also varies:
- AS affects men more frequently than women (3:1 ratio)
- RA is more common in women than men (3:1 ratio)
Distinct symptoms and progression
While both conditions cause joint pain and stiffness, they have unique characteristics:
- AS symptoms:
- Lower back pain and stiffness, especially in the morning
- Gradual fusion of vertebrae (bamboo spine)
- Eye inflammation (uveitis)
- RA symptoms:
- Symmetrical joint pain and swelling
- Morning stiffness lasting over an hour
- Fatigue and low-grade fever
Understanding these key differences is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. With this foundation, we can now explore the challenges in diagnosing these conditions.
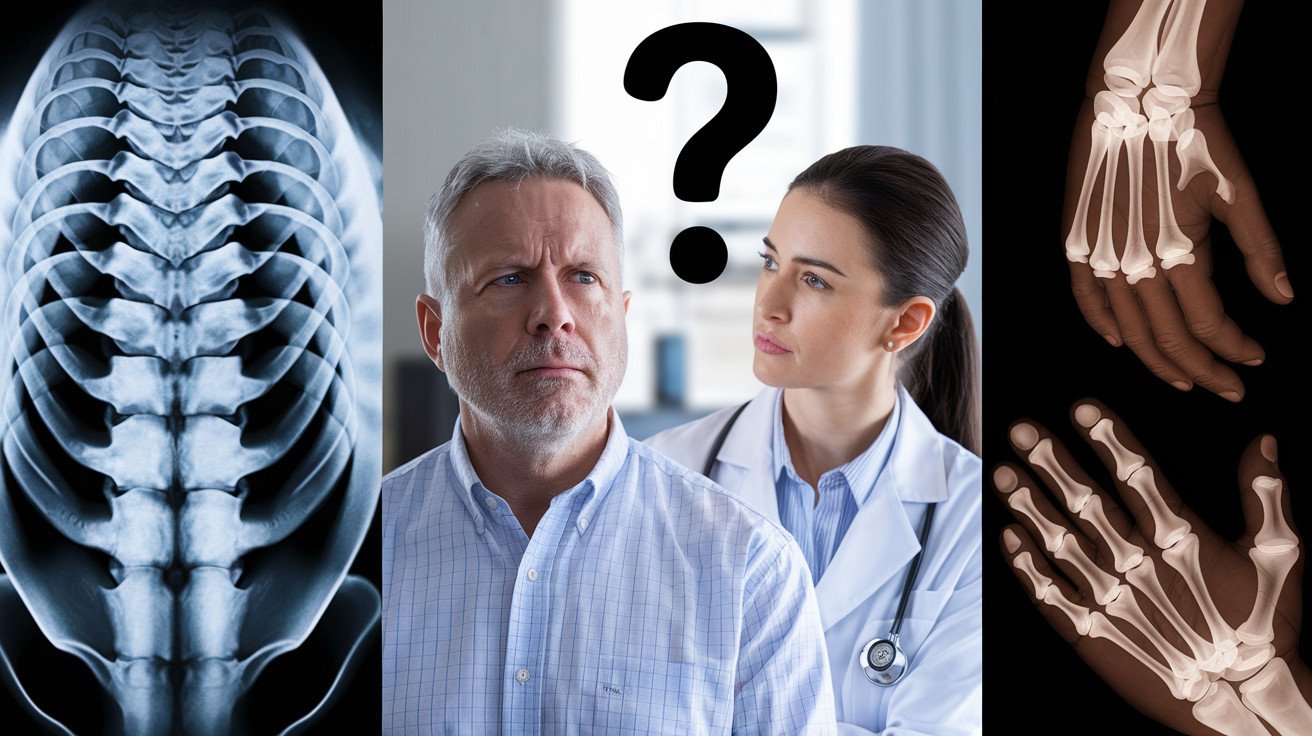


Diagnosis Challenges: Separating AS from RA
Now that we understand the basics of Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), let’s delve into the challenges of accurately diagnosing these conditions. Distinguishing between AS and RA can be complex, but it’s crucial for effective treatment.
Role of rheumatologists in accurate diagnosis
Rheumatologists play a pivotal role in accurately diagnosing AS and RA. Their expertise is essential because:
- They have specialized knowledge of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions
- They can interpret complex symptoms and test results
- They stay updated on the latest diagnostic criteria and treatment options
Importance of early detection
Early detection is critical for both AS and RA. Here’s why:
- It allows for prompt treatment initiation
- It can slow disease progression and prevent joint damage
- It improves long-term outcomes and quality of life
Essential diagnostic tests and imaging
Several tests and imaging techniques are used to diagnose AS and RA:
| Test/Imaging | AS | RA |
|---|---|---|
| X-rays | Shows sacroiliac joint changes | Reveals joint erosions |
| MRI | Detects early inflammation | Identifies synovitis |
| Blood tests | HLA-B27 genetic marker | Rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP antibodies |
| Physical exam | Assesses spinal mobility | Evaluates joint swelling and tenderness |
Common misdiagnosis pitfalls
Misdiagnosis can occur due to several factors:
- Overlapping symptoms between AS and RA
- Similarity to other conditions like psoriatic arthritis or fibromyalgia
- Atypical presentation in some patients
- Lack of definitive single diagnostic test
To avoid these pitfalls, a comprehensive approach combining clinical evaluation, imaging, and laboratory tests is essential. With this understanding of the diagnostic challenges, let’s explore how these conditions impact patients’ quality of life.
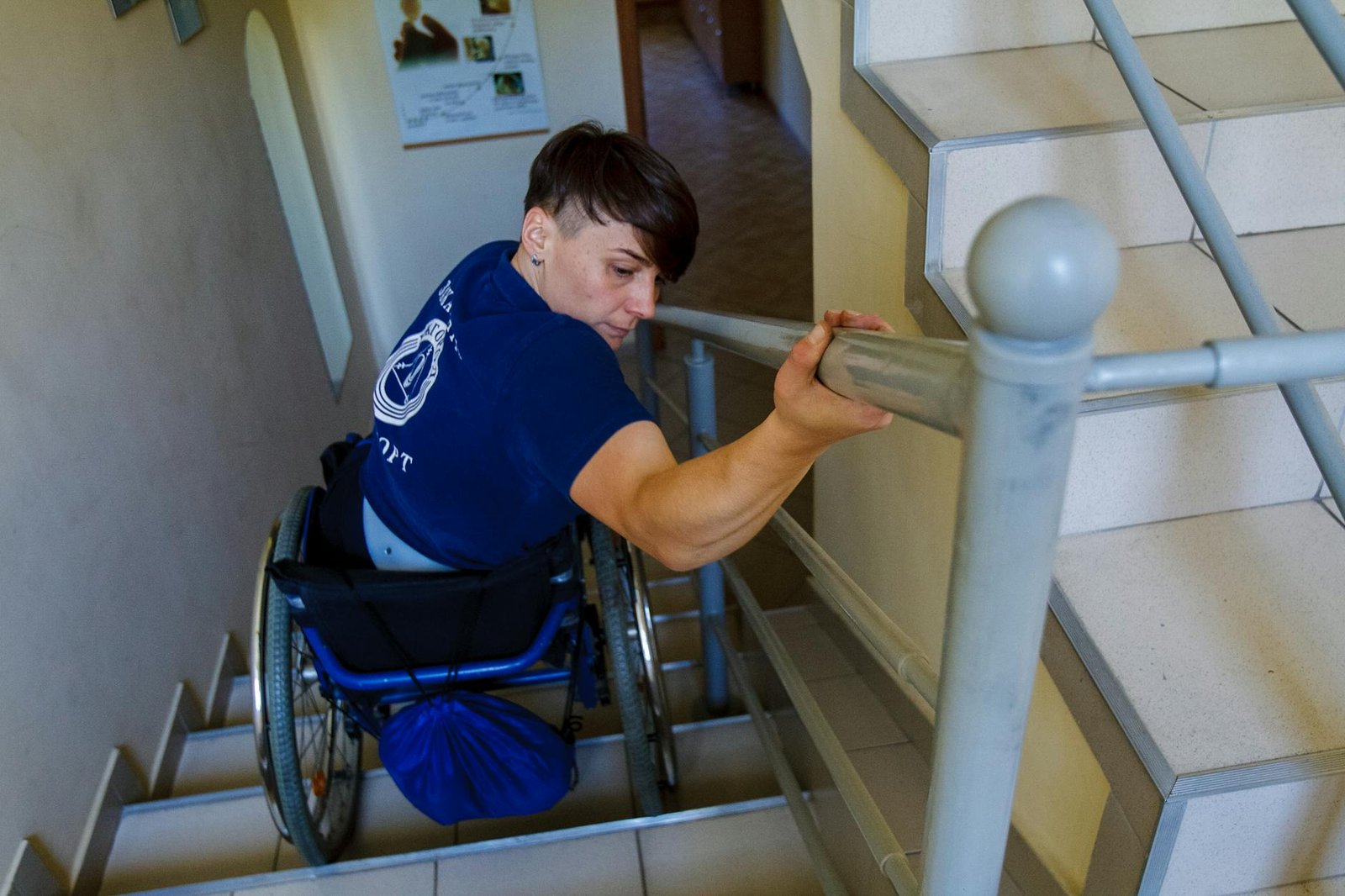


Impact on Quality of Life
Both Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) significantly affect a person’s quality of life, albeit in different ways. Let’s explore the various aspects of daily living impacted by these conditions.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Living with chronic conditions like AS or RA can take a toll on mental health. Patients often experience:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Frustration
- Low self-esteem
These emotional challenges can be as debilitating as the physical symptoms, making psychological support crucial in managing both AS and RA.
Work and Lifestyle Adjustments
AS and RA often necessitate significant changes in work and daily routines:
- Flexible work hours
- Ergonomic workstations
- Regular breaks for stretching or rest
- Career changes in severe cases
| Adjustment | AS | RA |
|---|---|---|
| Workspace modifications | Standing desks, supportive chairs | Ergonomic tools, voice recognition software |
| Schedule changes | Morning stiffness may delay start times | Fatigue may require shorter work days |
| Physical demands | Limited heavy lifting or prolonged standing | Reduced fine motor tasks |
Mobility Limitations and Adaptations
Both conditions can restrict movement, but in different ways:
- AS primarily affects the spine and large joints
- RA typically impacts smaller joints in hands and feet
Adaptations might include:
- Assistive devices (canes, walkers)
- Home modifications (grab bars, raised toilet seats)
- Adaptive clothing and footwear
Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain management is crucial for maintaining quality of life. Strategies may include:
- Medications (NSAIDs, DMARDs, biologics)
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Heat and cold therapy
- Stress reduction techniques (meditation, yoga)
- Alternative therapies (acupuncture, massage)
Understanding these impacts is crucial for patients and caregivers alike. With proper management and support, individuals with AS or RA can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by their condition. Next, we’ll explore the tailored treatment approaches for each condition.


Treatment Approaches: Tailored Care
When it comes to managing Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), tailored care is essential. Let’s explore the various treatment approaches available for these conditions.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Researchers are continuously working on developing new therapies for AS and RA. Some promising areas include:
- Targeted biologics
- JAK inhibitors
- Gene therapy
| Treatment Type | AS | RA |
|---|---|---|
| Biologics | ✓ | ✓ |
| JAK Inhibitors | ✓ | ✓ |
| Gene Therapy | 🔬 | 🔬 |
(✓ = Approved, 🔬 = In clinical trials)
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Many patients find relief through alternative therapies, such as:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Herbal supplements
- Mindfulness meditation
Surgical Interventions: When and Why
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Common procedures include:
- Joint replacement
- Spinal fusion (for AS)
- Synovectomy (for RA)
Physical Therapy and Exercise Regimens
Regular exercise and physical therapy play a crucial role in managing both AS and RA. Key components include:
- Stretching exercises
- Low-impact aerobic activities
- Strength training
- Posture improvement techniques
Medications for AS and RA
Both conditions often require medication to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Common medications include:
- NSAIDs
- DMARDs
- Corticosteroids
- Biologics
While AS and RA share some treatment approaches, the specific regimen must be tailored to each individual’s needs and disease progression. Regular consultation with a rheumatologist is essential for optimal management. Now that we’ve covered treatment approaches, let’s explore some practical tips for living with AS or RA.


Living with AS or RA: Practical Tips
Now that we’ve explored the treatment approaches for Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), let’s focus on practical tips to help you manage daily life with these conditions.
A. Adaptive tools and home modifications
Living with AS or RA can be challenging, but various adaptive tools and home modifications can significantly improve your quality of life:
- Ergonomic kitchen utensils with larger grips
- Shower chairs and grab bars in the bathroom
- Raised toilet seats
- Long-handled reachers for picking up objects
- Electric can openers and jar openers
| Room | Modification | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Kitchen | Lowered countertops | Reduces strain on back and joints |
| Bedroom | Adjustable bed | Improves sleep quality and comfort |
| Bathroom | Walk-in shower | Enhances safety and accessibility |
B. Support groups and resources
Connecting with others who understand your experience can be invaluable. Consider:
- Joining local or online support groups
- Participating in arthritis-focused forums
- Attending educational seminars on AS or RA
- Utilizing resources from organizations like the Arthritis Foundation or Spondylitis Association of America
C. Stress management techniques
Managing stress is crucial for both AS and RA patients. Try these techniques:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Gentle yoga or tai chi
- Regular exercise routines
- Journaling or art therapy
D. Nutrition and diet recommendations
While there’s no specific diet for AS or RA, certain nutritional choices may help manage symptoms:
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 rich fish, leafy greens, and berries
- Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars
- Stay hydrated with water and herbal teas
- Consider supplements like vitamin D and calcium (consult with your doctor first)
By implementing these practical tips, you can better manage your AS or RA symptoms and improve your overall quality of life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your routine or diet.

Ankylosing Spondylitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis, while sharing some similarities, are distinct conditions that require different approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and management. Understanding the unique characteristics of each condition is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. From the initial symptoms to the long-term impact on quality of life, recognizing the differences between AS and RA can lead to more accurate diagnoses and more effective treatment plans.
As we navigate the complexities of these autoimmune disorders, it’s clear that a personalized approach is key. Whether you’re dealing with AS or RA, working closely with your healthcare team, staying informed about your condition, and implementing practical strategies for daily living can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, while these conditions may present challenges, with the right support and management, many individuals with AS or RA lead fulfilling, active lives.
Read more about AS